Pay stubs, also known as paycheck stubs or payslips, are important documents that provide employees with detailed information about their earnings and deductions. Understanding pay stubs is essential for financial planning, tax filing, and ensuring accurate compensation. In this article, we will explore the key aspects of pay stubs and the information they provide.
Purpose of a Pay Stub
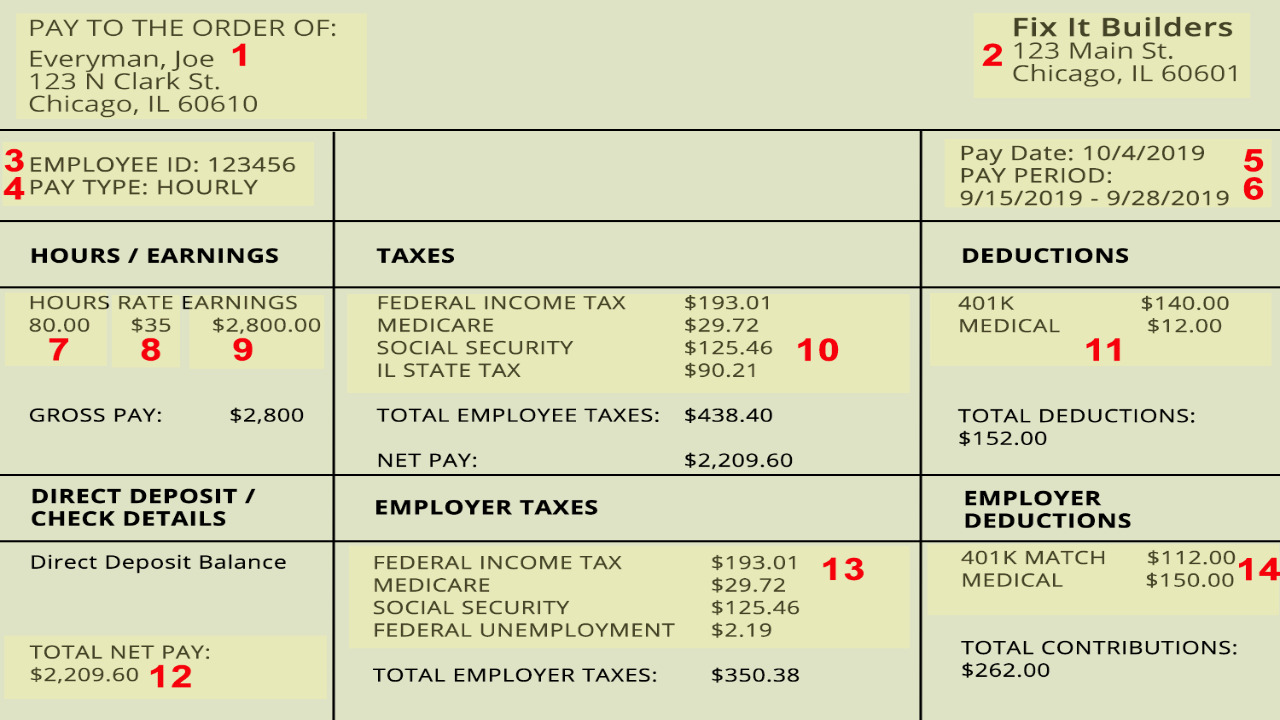
A pay stub serves as a record of an employee’s earnings and deductions for a specific pay period. It provides transparency and helps employees understand how their paycheck is calculated. Pay stubs also serve as proof of income and are often required for various financial transactions, such as applying for loans or renting an apartment. You can find free pay stub templates here and make the whole process of submitting smoother.
Basic Information
The pay stub typically includes basic information about the employee and the employer. This includes the employee’s name, address, and social security number and the employer’s name, address, and identification number. It also specifies the pay period covered by the stub, such as weekly, biweekly, or monthly.
Earnings
One of the most important sections of a pay stub is the earnings section. It details the employee’s gross wages, which is the total amount earned before any deductions. It may also include additional earnings, such as overtime pay, bonuses, or commissions. The pay stub should clearly state the rate of pay, the number of hours worked, and any applicable rates for different types of work.
Deductions

Deductions are the amounts subtracted from an employee’s gross wages to calculate the net pay. Common deductions include federal, state, and local taxes, as well as Social Security and Medicare contributions. Other deductions may include health insurance premiums, retirement contributions, and voluntary deductions like charitable donations or union dues. Each deduction should be clearly labeled and accompanied by the corresponding amount.
Taxes
Pay stubs provide detailed information about various taxes withheld from an employee’s wages. This includes federal income tax, state income tax (if applicable), and local taxes. The pay stub may also indicate the employee’s filing status and allowances claimed on their W-4 form, which determines the amount of tax withheld. Understanding the tax withholding on a pay stub is crucial for accurate tax planning and filing.
Benefits and Contributions

Many employers offer benefits and retirement plans to their employees, and pay stubs often include information about these contributions. This may include deductions for health insurance premiums, retirement plan contributions (such as 401(k) or IRA), and flexible spending accounts (FSAs) for healthcare or dependent care expenses. It is important to review these deductions to ensure they align with the chosen benefits and retirement contributions.
Net Pay
The net pay is the amount the employee receives after all deductions have been subtracted from their gross wages. It is the actual amount that will be deposited into the employee’s bank account or given in a physical paycheck. The pay stub should clearly display the net pay, ensuring transparency and accuracy in compensation.
YTD (Year-to-Date) Information
Pay stubs often include a year-to-date (YTD) section that summarizes the employee’s earnings and deductions for the current calendar year. It provides a snapshot of the employee’s total earnings and deductions since the beginning of the year, which can be useful for budgeting, tax planning, and financial analysis.
In conclusion, understanding pay stubs is essential for employees to monitor their earnings, deductions, and overall financial well-being. By examining the various sections of a pay stub, such as earnings, deductions, taxes, benefits, and net pay, employees can ensure accuracy, plan for taxes, and make informed financial decisions. Regularly reviewing pay stubs can help individuals stay financially organized and prepared.

